Kliensoldali webprogramozás
Redux
Horváth Győző
Egyetemi docens
1117 Budapest, Pázmány Péter sétány 1/c., 2.408-as szoba
Tel: (1) 372-2500/8469
horvath.gyozo@inf.elte.hu
Ismétlés
React
- Komponensalapú webfejlesztés
ui = f(state)- Komponensek: függvények
- Alkalmazás: függvénykompozíció
- Hooks: szolgáltatások függvényként

Adatok
- Állapottér
- Külső adat:
props - Belső adat:
state - Adat helye
- Adat megosztása
- prop drilling
- kompozíció
- context
- Adatfolyás iránya
- data down
- action up
További információk
- Hook-ok
- Állapotkezelés, adat helye
- Context
- Adattárolás
- Optimalizáció
Architektúra koncepciók
Komplexitás kezelése
Karbantarthatóság
Adat és struktúra
Data flow
Kontextus
- 2006: jQuery
- 2010: SPA, MV*
- 2014: React
De! MVC egy architekturális minta, a React egy nézet függvénykönyvtár
→ Kell egy architektúra koncepció a React mellé!
Kiindulási pont: MVC


Kétirányú adatkötés
- Probléma forrása: az adatfolyás iránya
- Komplex háló, nehéz debugolni, aszinkron folyamatok



Megoldás: egyirányú adatfolyam
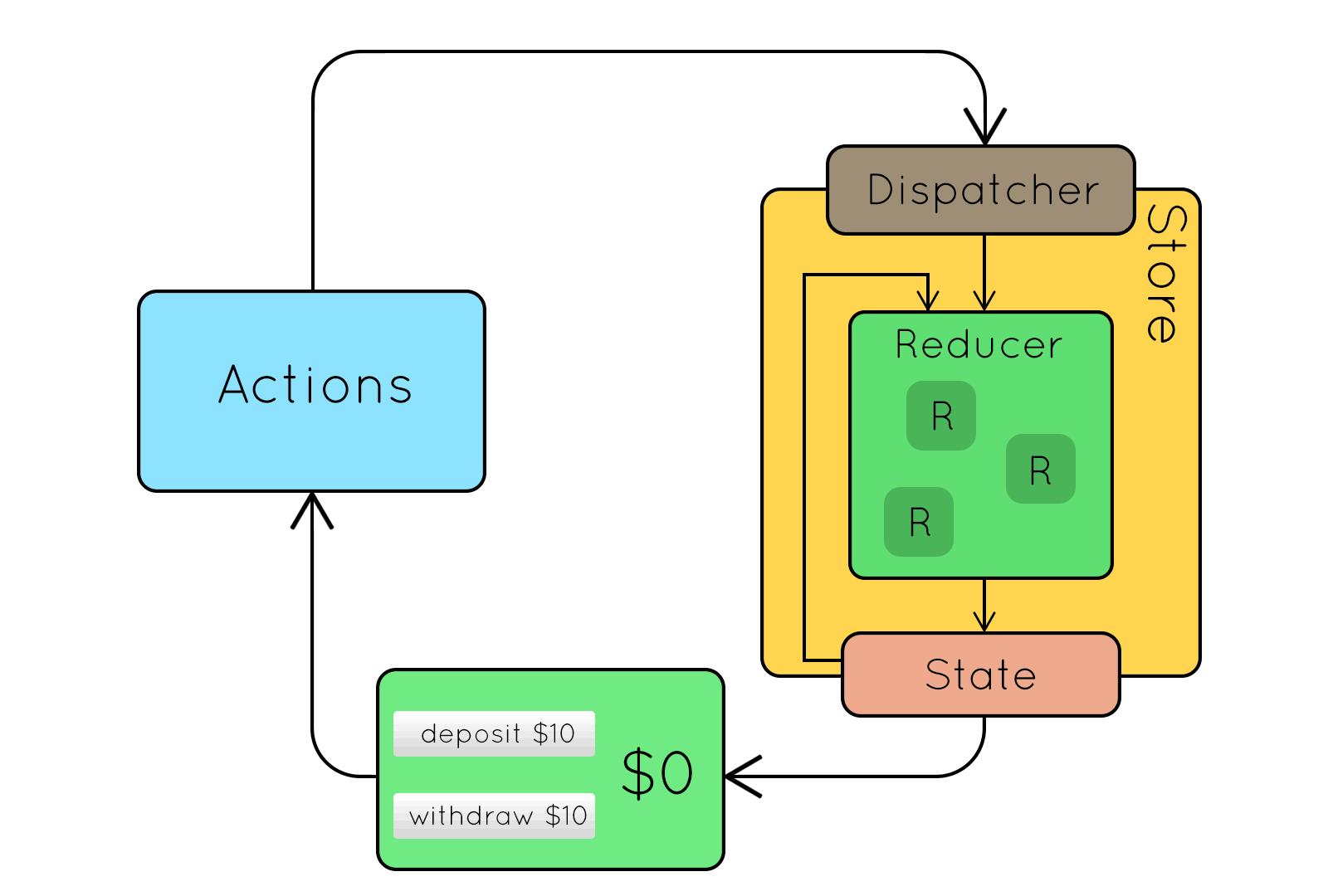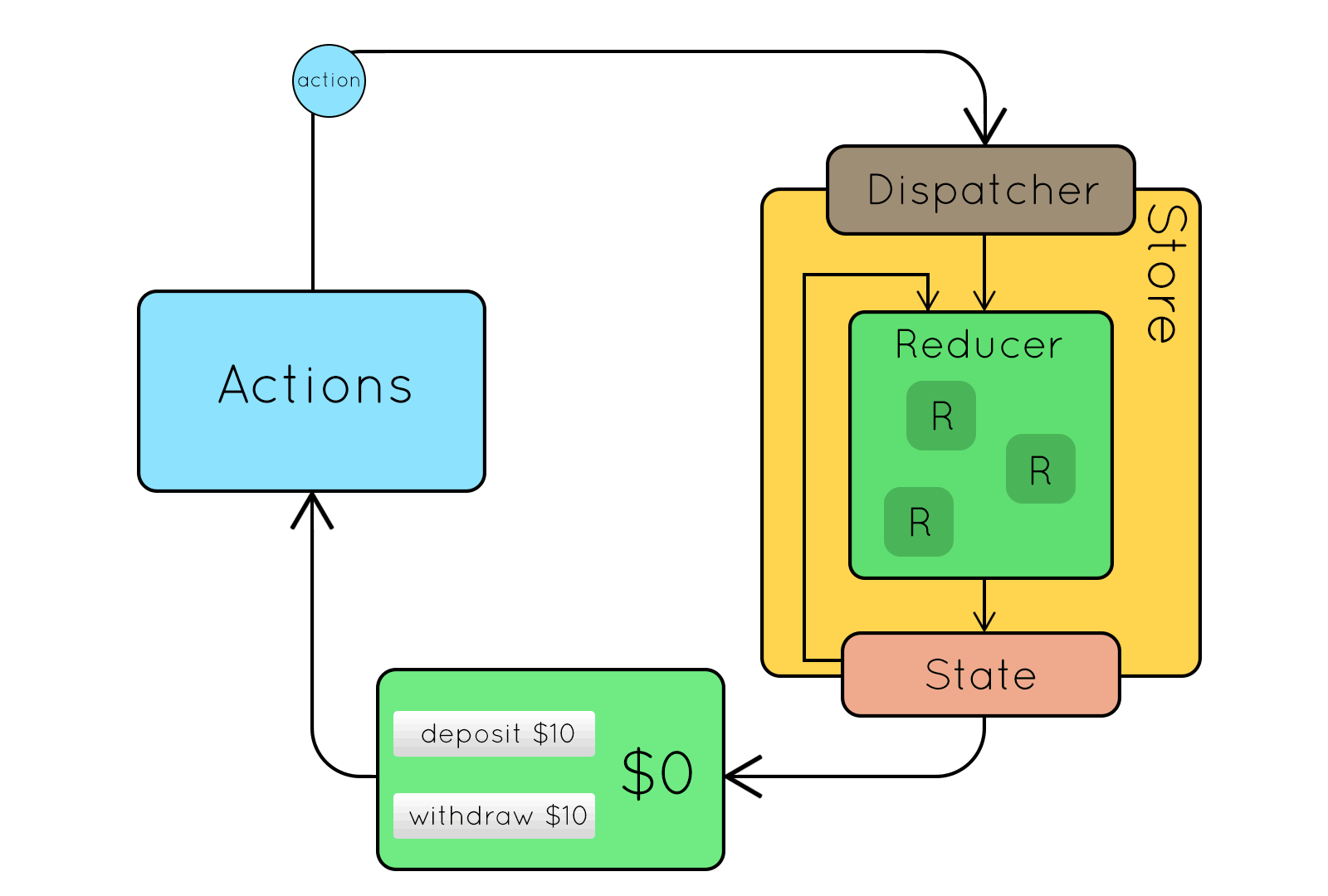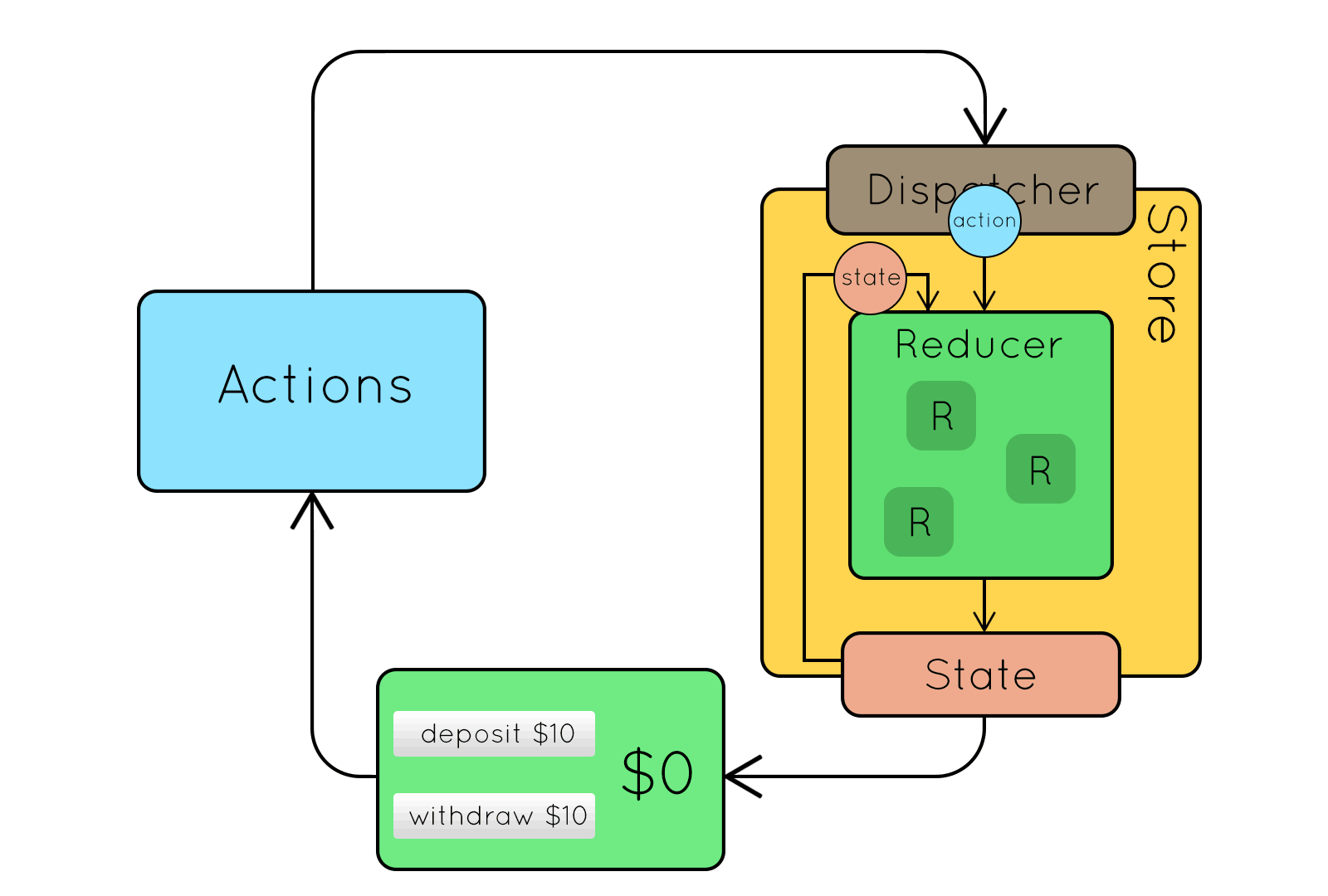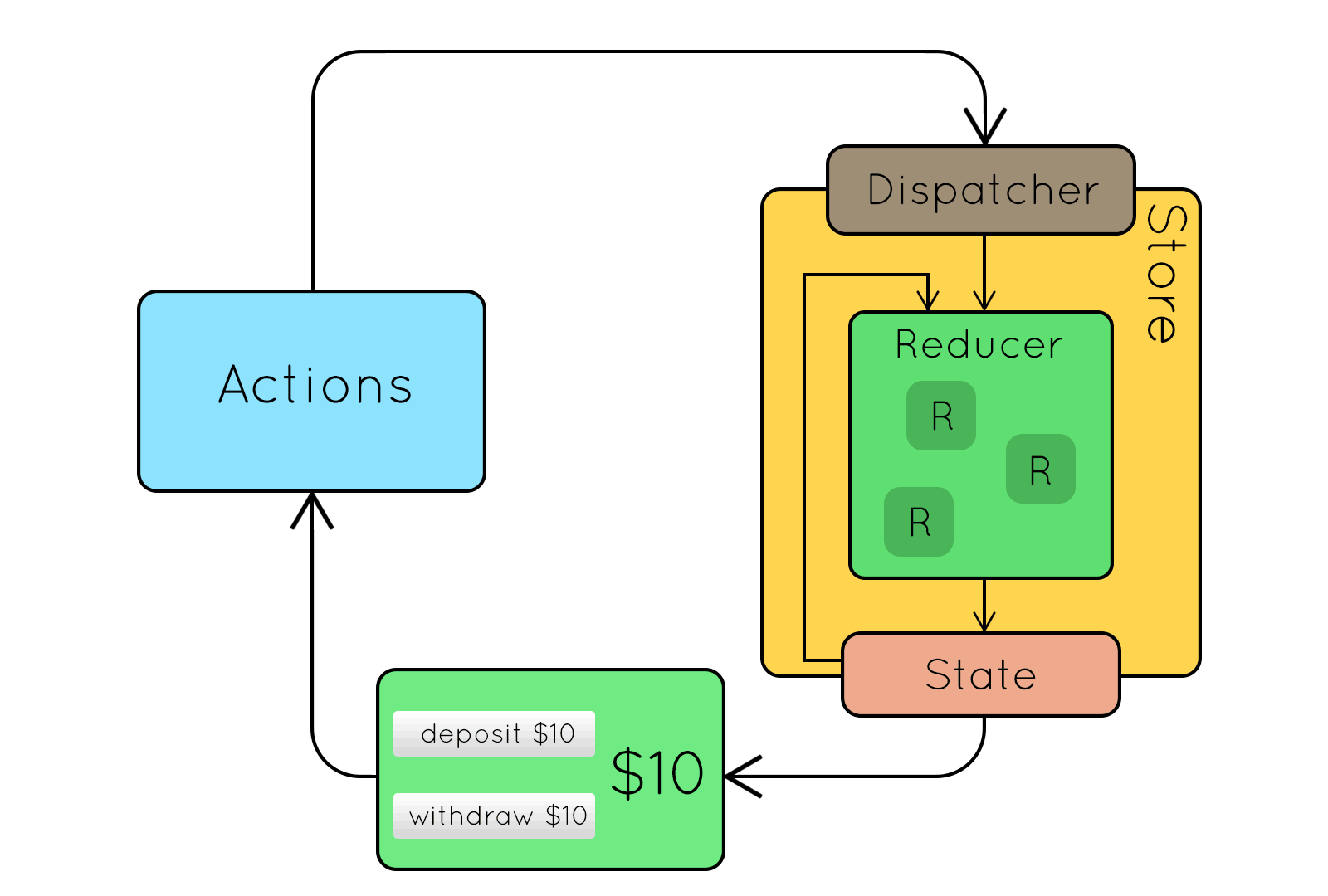
Flux
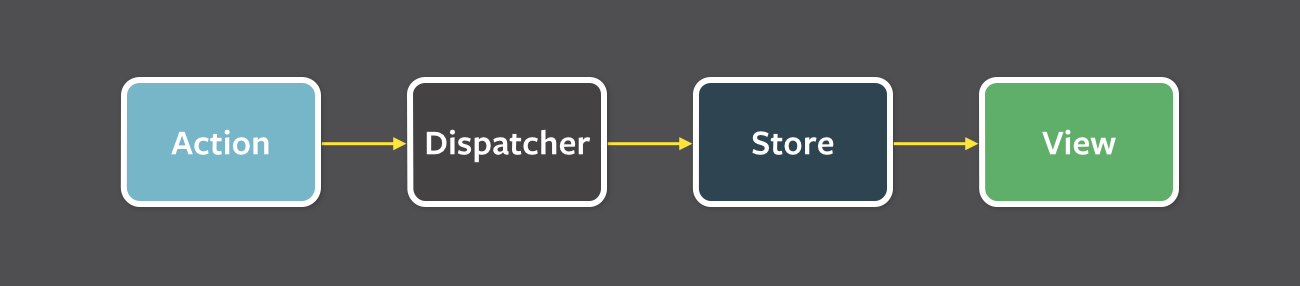

Flux jellegzetességek
- Egyirányú adatfolyam
- Kiszámítható működés
- Dispatcher: központi eseménykezelő
- Kikényszerített szinkronitás
- minden aszinkron művelet actiont dob
- Inversion of Control
- csak a store felelős az állapotának változtatásáért
- Szemantikus akciók
- Egyszerre egy akció
Flux

Flux
Kívülről jövő action
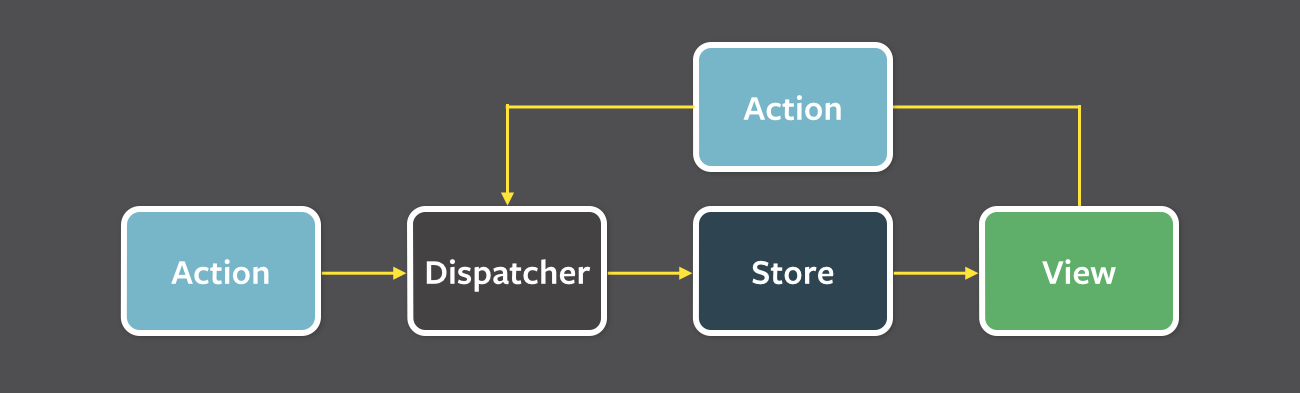
Flux

Redux
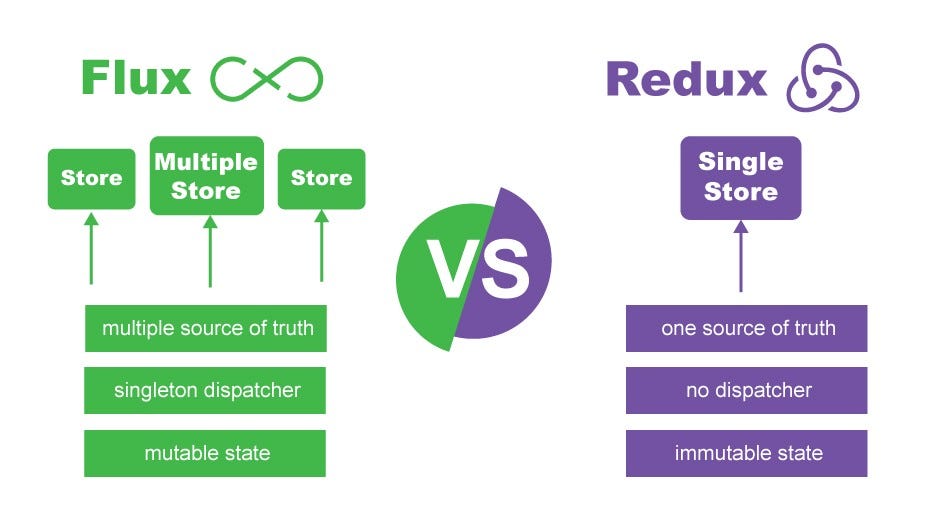
Flux hátránya
- több store, függőségek nehézkes kezelése
- → egy store legyen!
- → dispatcher beépíthető a store-ba
- store: adat + metódus
- nehéz az adatot lecserélni
- mutábilis állapot
- nehéz a folyamatot időben követni
- nehéz bővíteni harmadik féltől származó kiegészítéssel
Hot reload


Time travel debugging


Több store

Flux vs Redux

Flux vs Redux
Motiváció
- Kliensoldali adat sok és sokféle
- átlátható, determinisztikus működés
- UX fejlesztések, mint pl. optimista módosítás
- Nehezíti: mutáció és aszinkronitás
- Nézet réteg OK: React
- Adatrétegnek mi ad struktúrát → Redux
- Kiszámítható állapotváltozások
Központi koncepciók
- State: állapottér mint egyetlen objektum
- Action: módosító parancsok mint objektumok
- Action creator: Action-öket előállító tiszta függvény
- Reducer:
(state, action) → newState - Store: State + Dispatcher + Reducer
Redux
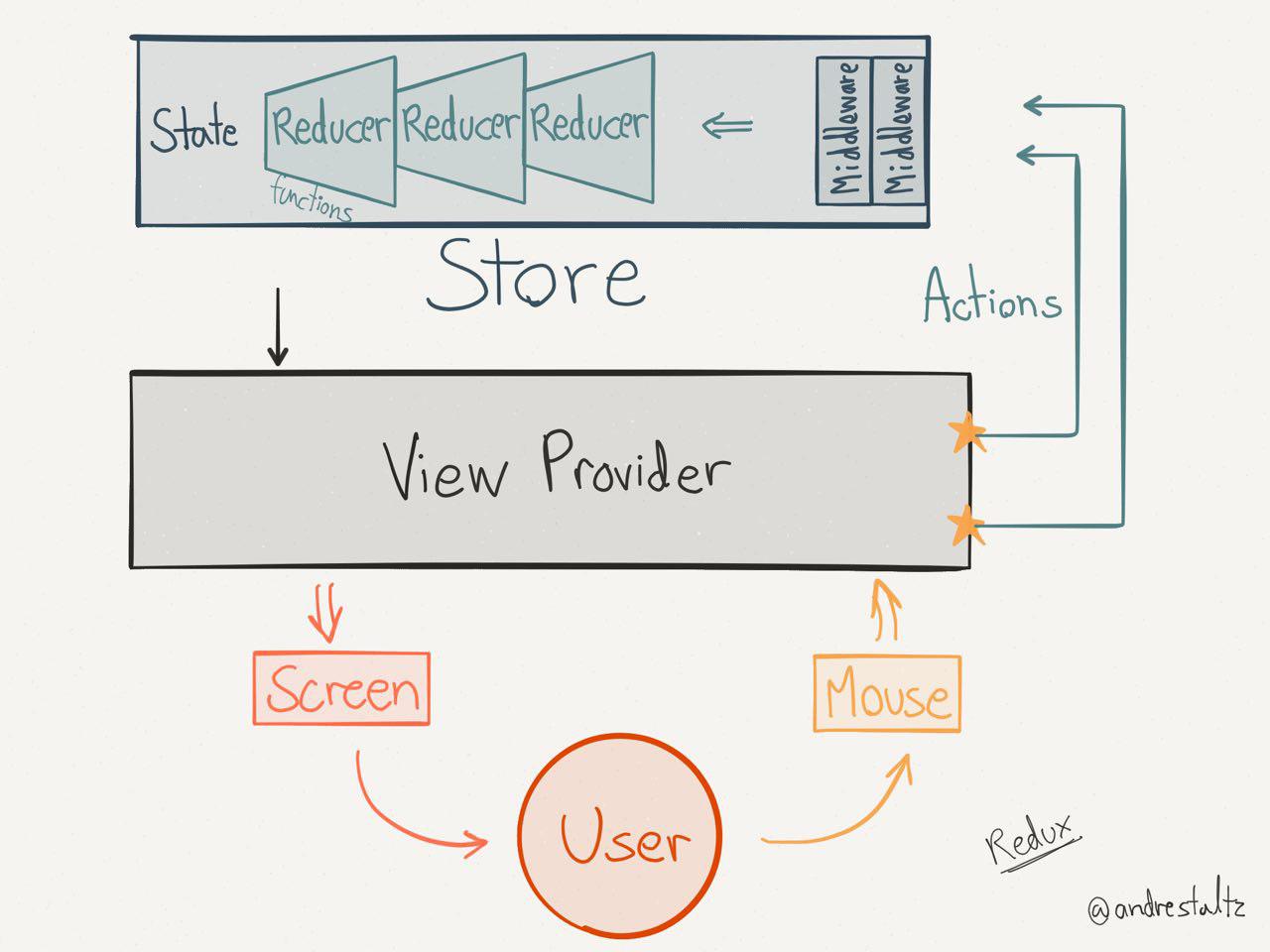
Állapottér
{
todos: [{
text: 'Eat food',
completed: true
}, {
text: 'Exercise',
completed: false
}],
visibilityFilter: 'SHOW_COMPLETED'
}Action és Action creator
// Action
{ type: 'ADD_TODO', text: 'Go to swimming pool' }// Action type
const ADD_TODO = 'ADD_TODO'
// Action
{
type: ADD_TODO,
text: 'Build my first Redux app'
}// Action creator
function addTodo(text) {
return {
type: ADD_TODO,
text
}
}Reducer
function reducer(state = initialState, action) {
// Create the new state
return state
}function todoApp(state = initialState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case SET_VISIBILITY_FILTER:
return Object.assign({}, state, {
visibilityFilter: action.filter
})
case ADD_TODO:
return Object.assign({}, state, {
todos: [
...state.todos,
{
text: action.text,
completed: false
}
]
})
case TOGGLE_TODO:
return Object.assign({}, state, {
todos: state.todos.map((todo, index) => {
if (index === action.index) {
return Object.assign({}, todo, {
completed: !todo.completed
})
}
return todo
})
})
default:
return state
}
}Store
const store = createStore(reducer)import {
addTodo,
toggleTodo,
setVisibilityFilter,
VisibilityFilters
} from './actions'
const store = createStore(todoApp)
// Log the initial state
console.log(store.getState())
// Every time the state changes, log it
// Note that subscribe() returns a function for unregistering the listener
const unsubscribe = store.subscribe(() => console.log(store.getState()))
// Dispatch some actions
store.dispatch(addTodo('Learn about actions'))
store.dispatch(addTodo('Learn about reducers'))
store.dispatch(addTodo('Learn about store'))
store.dispatch(toggleTodo(0))
store.dispatch(toggleTodo(1))
store.dispatch(setVisibilityFilter(VisibilityFilters.SHOW_COMPLETED))
// Stop listening to state updates
unsubscribe()Három alapelv
- Az állapottér egyetlen komplex objektum
- csak adat
- az alkalmazás adatleírása
- Az állapottér csak olvasható
- immutábilis
- csak akción keresztül változtatható meg
- A reducer tiszta függvény
- tesztelhető
- funkcionális paradigma
React-redux
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from 'react-redux'
import { toggleTodo } from '../actions'
const getVisibleTodos = (todos, filter) => {
switch (filter) {
case 'SHOW_ALL':
return todos
case 'SHOW_COMPLETED':
return todos.filter(t => t.completed)
case 'SHOW_ACTIVE':
return todos.filter(t => !t.completed)
}
}
const selectTodos = state => getVisibleTodos(state.todos, state.visibilityFilter)
export const TodoList = () => {
const todos = useSelector(selectTodos)
const dispatch = useDispatch()
return (
<ul>{todos.map((todo, index) => (
<Todo key={index} {...todo} onClick={() => dispatch(toggleTodo(index))} />
))}
</ul>
)
}Redux
Redux gondolkodás
Akasztófa játék
(Egyszerű feladat)
Lépések
- Redux-független állapottér
- Állapottér átgondolása
- Állapotátmenetek
- Lekérdezések
- Tesztelhető
- Redux
- actions + action creators
- reducer(s)
- store
- CLI tesztelés
- React
- komponensek
- selectors
- dispatch actions
Állapottér
const getInitialState = () => ({
word: 'apple',
tips: [],
letters: 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'.split(''),
maxTips: 9,
})Állapotátmenetek és lekérdezések
// Állapotátmenetek (tiszta függvény, tesztelhető)
function makeATip(tips, letter) {
return tips.concat(letter)
}
// or
function makeATip(state, letter) {
return {...state, tips: state.tips.concat(letter)}
}// Lekérdezések (tiszta függvény, tesztelhető)
function getIsWon(word, tips) {
return Array.from(word).every(l => tips.includes(l))
}
function getIsLost(tips, word, maxTips) {
return getBadTips(tips, word).length === maxTips
}
function getBadTips(tips, word) {
return tips.filter(l => !word.includes(l))
}Redux actions és action creators
// Action types
const MAKE_TIP = 'MAKE_TIP'
const START_AGAIN = 'START_AGAIN'
// Action creators
const makeTip = letter => ({
type: MAKE_TIP,
payload: letter,
})
const startAgain = () => ({
type: START_AGAIN
})Reducer
const rootReducer = (state = getInitialState(), action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case MAKE_TIP:
return {...state,
tips: makeATip(state.tips, action.payload)
}
case START_AGAIN:
return getInitialState()
default:
return state
}
}Store és tesztelés
import { createStore } from "redux"
const store = createStore(rootReducer, getInitialState())console.log(store.getState())
const unsubscribe = store.subscribe(() => console.log(store.getState()))
// Dispatch some actions
store.dispatch(makeTip('a'))
store.dispatch(makeTip('b'))
store.dispatch(startAgain())
unsubscribe()Reducer variációk
// Állapot
{ word: 'apple',
tips: [],
letters: ['a', 'b', 'c'],
maxTips: 9, }const wordReducer = (state = 'apple', action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case START_AGAIN:
return newWord()
}
return state
}
const tipsReducer = (state = [], action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case MAKE_TIP:
return makeATip(state, action.payload)
case START_AGAIN:
return []
}
return state
}
const lettersReducer = (state = ['a', 'b', 'c'], action) => state
const maxTipsReducer = (state = 9, action) => state Reducer variációk
const rootReducer = (state = {}, action) => ({
word: wordReducer(state.word, action),
tips: tipsReducer(state.tips, action),
letters: lettersReducer(state.letters, action),
maxTips: maxTipsReducer(state.maxTips, action),
})import { combineReducers } from "redux"
const rootReducer = combineReducers({
word: wordReducer,
tips: tipsReducer,
letters: lettersReducer,
maxTips: maxTipsReducer,
})Reducer variációk
const tips = (state = [], action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case MAKE_TIP:
return makeATip(state, action.payload)
}
return state
}
const word = (state = 'apple', action) => state
const letters = (state = ['a', 'b', 'c'], action) => state
const maxTips = (state = 9, action) => state const combinedReducer = combineReducers({ word, tips, letters, maxTips })
const startAgainReducer = (state, action) => action.type === START_AGAIN
? getInitialState()
: state
const rootReducer = (state, action) => {
const intermediateState = combinedReducer(state, action)
const finalState = startAgainReducer(intermediateState, action)
return finalState
}Store provider
import { Provider } from "react-redux"
const App = () => (
<Provider store={store}>
<h1>Hangman</h1>
<Word />
<Buttons />
<Result />
<Hangman />
</Provider>
)<Word>
// Selectors
const getWordLetters = ({word, tips, maxTips}) => word.split('').map(letter => ({
letter,
visible: getIsLost(tips, word, maxTips) || tips.includes(letter),
missing: getIsLost(tips, word, maxTips) && tips.includes(letter),
}))
const getGameState = ({word, tips, maxTips}) => ({
won: getIsWon(word, tips),
lost: getIsLost(tips, word, maxTips)
})import { useSelector } from "react-redux"
const Word = () => {
const letters = useSelector(getWordLetters)
const { won } = useSelector(getGameState)
return (
<div id="szo" className={cn({nyer: won})}>
{letters.map(({letter, missing, visible}, i) =>
<span key={i} className={cn({hianyzo: missing})}>{visible && letter}</span>
)}
</div>
)
}<Buttons>
const getButtons = ({letters, tips}) => letters.map(letter => ({
letter,
disabled: tips.includes(letter)
}))
const getGameState = ({word, tips, maxTips}) => ({
won: getIsWon(word, tips),
lost: getIsLost(tips, word, maxTips)
})const Buttons = () => {
const buttons = useSelector(getButtons)
const { won, lost } = useSelector(getGameState)
const dispatch = useDispatch()
const handleClick = letter => dispatch(makeTip(letter))
if (won || lost) {
return <button onClick={() => dispatch(startAgain())}>Start again</button>
}
return (
<div id="betuk">
{buttons.map(({letter, disabled}) =>
<button onClick={() => handleClick(letter)} key={letter} disabled={disabled}>{letter}</button>
)}
</div>
)
}Result
const getResult = ({tips, word, maxTips}) => ({
wrong: getBadTips(tips, word).length,
maxTips: maxTips,
})const Result = () => {
const { wrong, maxTips } = useSelector(getResult)
return (
<div id="eredmeny">
{wrong}/{maxTips}
</div>
)
}<Hangman>
const getResult = ({tips, word, maxTips}) => ({
wrong: getBadTips(tips, word).length,
maxTips: maxTips,
})const Hangman = () => {
const { wrong } = useSelector(getResult)
const parts = [
<line x1="0" y1="99%" x2="100%" y2="99%" key={1} />,
<line x1="20%" y1="99%" x2="20%" y2="5%" key={2} />,
<line x1="20%" y1="5%" x2="60%" y2="5%" key={3} />,
<line x1="60%" y1="5%" x2="60%" y2="20%" key={4} />,
<circle cx="60%" cy="30%" r="10%" key={5} />,
<line x1="60%" y1="30%" x2="60%" y2="70%" key={6} />,
<line x1="40%" y1="50%" x2="80%" y2="50%" key={7} />,
<line x1="60%" y1="70%" x2="50%" y2="90%" key={8} />,
<line x1="60%" y1="70%" x2="70%" y2="90%" key={9} />,
]
const partsToShow = parts.slice(0, wrong)
return (
<svg width="200px" height="200px" stroke="black">
{partsToShow}
</svg>
)
}Redux Devtools
useReducer
hook
useReducer
useStatealternatívája- komplex állapotlogika esetén
- ha az új state az előzőtől függ
- hatékonyabb megoldást ad
dispatchleküldése- callback-ek helyett
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initialArg, init);useReducer
const initialState = {count: 0};
function reducer(state, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'increment':
return {count: state.count + 1};
case 'decrement':
return {count: state.count - 1};
default:
throw new Error();
}
}
function Counter() {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initialState);
return (
<>
Count: {state.count}
<button onClick={() => dispatch({type: 'decrement'})}>-</button>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({type: 'increment'})}>+</button>
</>
);
}Callback-ek helyett
const TodosDispatch = React.createContext(null);
function TodosApp() {
// Note: `dispatch` won't change between re-renders
const [todos, dispatch] = useReducer(todosReducer);
return (
<TodosDispatch.Provider value={dispatch}>
<DeepTree todos={todos} />
</TodosDispatch.Provider>
);
}function DeepChild(props) {
// If we want to perform an action, we can get dispatch from context.
const dispatch = useContext(TodosDispatch);
function handleClick() {
dispatch({ type: 'add', text: 'hello' });
}
return (
<button onClick={handleClick}>Add todo</button>
);
}Redux toolkit
npm install @reduxjs/toolkitStore létrehozása
import { applyMiddleware, createStore } from 'redux'
import { composeWithDevTools } from 'redux-devtools-extension'
import thunkMiddleware from 'redux-thunk'
import monitorReducersEnhancer from './enhancers/monitorReducers'
import loggerMiddleware from './middleware/logger'
import rootReducer from './reducers'
export default function configureStore(preloadedState) {
const middlewares = [loggerMiddleware, thunkMiddleware]
const middlewareEnhancer = applyMiddleware(...middlewares)
const enhancers = [middlewareEnhancer, monitorReducersEnhancer]
const composedEnhancers = composeWithDevTools(...enhancers)
const store = createStore(rootReducer, preloadedState, composedEnhancers)
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && module.hot) {
module.hot.accept('./reducers', () => store.replaceReducer(rootReducer))
}
return store
}configureStore
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
import rootReducer from './reducers'
const store = configureStore({
reducer: rootReducer,
})
export default storeReducer
switch, immutábilis megoldások
const initialState = { value: 0 }
function counterReducer(state = initialState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'increment':
return { ...state, value: state.value + 1 }
case 'decrement':
return { ...state, value: state.value - 1 }
case 'incrementByAmount':
return { ...state, value: state.value + action.payload }
default:
return state
}
}createReducer
import { createAction, createReducer } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
const increment = createAction('counter/increment')
const decrement = createAction('counter/decrement')
const incrementByAmount = createAction('counter/incrementByAmount')
const initialState = { value: 0 }
const counterReducer = createReducer(initialState, (builder) => {
builder
.addCase(increment, (state, action) => {
state.value++
})
.addCase(decrement, (state, action) => {
state.value--
})
.addCase(incrementByAmount, (state, action) => {
state.value += action.payload
})
})createReducer
import { createAction, createReducer } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
const increment = createAction('increment')
const decrement = createAction('decrement')
function isActionWithNumberPayload(action) {
return typeof action.payload === 'number'
}
const reducer = createReducer(
{
counter: 0,
sumOfNumberPayloads: 0,
unhandledActions: 0,
},
(builder) => {
builder
.addCase(increment, (state, action) => {
// action is inferred correctly here
state.counter += action.payload
})
// You can chain calls, or have separate `builder.addCase()` lines each time
.addCase(decrement, (state, action) => {
state.counter -= action.payload
})
// You can apply a "matcher function" to incoming actions
.addMatcher(isActionWithNumberPayload, (state, action) => {})
// and provide a default case if no other handlers matched
.addDefaultCase((state, action) => {})
}
)Actions
const INCREMENT = 'counter/increment'
function increment(amount) {
return {
type: INCREMENT,
payload: amount,
}
}
const action = increment(3)
// { type: 'counter/increment', payload: 3 }createAction
import { createAction } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
const increment = createAction('counter/increment')
let action = increment()
// { type: 'counter/increment' }
action = increment(3)
// returns { type: 'counter/increment', payload: 3 }
console.log(increment.toString())
// 'counter/increment'createAction
Callback
import { createAction, nanoid } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
const addTodo = createAction('todos/add', function prepare(text) {
return {
payload: {
text,
id: nanoid(),
createdAt: new Date().toISOString(),
},
}
})
console.log(addTodo('Write more docs'))
/**
* {
* type: 'todos/add',
* payload: {
* text: 'Write more docs',
* id: '4AJvwMSWEHCchcWYga3dj',
* createdAt: '2019-10-03T07:53:36.581Z'
* }
* }
**/createSlice
import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
const initialState = { value: 0 }
const counterSlice = createSlice({
name: 'counter',
initialState,
reducers: {
increment(state) {
state.value++
},
decrement(state) {
state.value--
},
incrementByAmount(state, action) {
state.value += action.payload
},
},
})
export const { increment, decrement, incrementByAmount } = counterSlice.actions
export default counterSlice.reducercreateSlice
const incrementBy = createAction('incrementBy')
const decrementBy = createAction('decrementBy')
const counter = createSlice({
name: 'counter',
initialState: 0,
reducers: {
increment: (state) => state + 1,
decrement: (state) => state - 1,
multiply: {
reducer: (state, action) => state * action.payload,
prepare: (value) => ({ payload: value || 2 }), // fallback if the payload is a falsy value
},
},
// "builder callback API", recommended for TypeScript users
extraReducers: (builder) => {
builder.addCase(incrementBy, (state, action) => {
return state + action.payload
})
builder.addCase(decrementBy, (state, action) => {
return state - action.payload
})
},
})createSlice
Visszatérési érték
{
name : string,
reducer : ReducerFunction,
actions : Record<string, ActionCreator>,
caseReducers: Record<string, CaseReducer>.
getInitialState: () => State
}Végszó
- Az adat köré épül az alkalmazás
- Fontos az állapotkezelés
- Redux: tiszta elvekre épülő állapotkezelő függvénykönyvtár
- állapot = objektum
- immutábilis
- action hatására kerül új állapotba
- Redux gondolkodás
- Redux toolkit