Webprogramozás
Követelmények, JavaScript nyelvi elemek
Horváth Győző
egyetemi docens
horvath.gyozo@inf.elte.hu
1117 Budapest, Pázmány Péter sétány 1/c., 4.725
Dinamikus webprogramozás
STATIKUS ⚡ DINAMIKUS
Eddigi ismeretek
Statikus weblapok készítése: Webfejlesztés
- HTML5
- CSS 1, 2, 3
- Alapvető HTTP ismeretek
- CSS keretrendszerek (Bootstrap)
Kliens-szerver architektúra
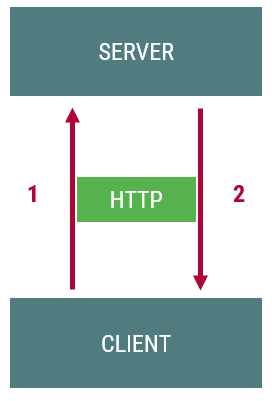
- Web: kliens és kiszolgáló kommunikációja
- HTTP: a kommunikáció protokollja
- URL: erőforrások azonosítója
- HTML: dokumentumleíró nyelv
- Lépések
- Kliens kérést intéz a szervernek
- Szerver válaszol
- A kliens feldolgozza a választ
Statikus oldalak
- Szerver szempontjából statikus
- Kérés pillanatában a szerveren megtalálható az a tartalom, amely leküldésre kerül a válaszban
- Fájlkiszolgálás
- Kliens szempontjából statikus
- A letöltött és a létrejött tartalom az oldal élettartamának a végéig ugyanaz
- Nem változik meg sem a böngésző állapota, sem a betöltött dokumentum szerkezete
- Nem fut le benne programkód, leíró nyelv, deklaratív
Dinamikus oldalak
- Szerver szempontjából dinamikus
- A válaszként leküldött tartalmat program állítja elő
- A kérés pillanatában a válasz még nem létezik a szerveren
- Kliens szempontjából dinamikus
- A letöltött tartalomban programkód fut le
- Ez megváltoztathatja a böngésző állapotát és a dokumentum szerkezetét
- ⇒ PROGRAMOZÁS
Miről lesz szó?
- Platformspecifikus programozás
- Dinamikus webprogramozás
- Kliens-szerver architektúra mindkét oldalán
- Kliensoldalon: JavaScript
- Szerveroldalon: PHP
- Alapvető ismeretek, bevezetés
- Új nyelvek
- Új technológiák
- Új programozási modellek
Félév felépítése
- Kliens oldali dinamikus webprogramozás: JavaScript
- Szerver oldali dinamikus webprogramozás: PHP
Motiváció
Követelmények
Információk a tárgyról
- Követelmények
- Előadások (dia, videó)
- Gyakorlati videók
- Gyakorlati anyagok (feladatsor)
- Beadandók
- ZH-k
- Eredmények
Kliensoldali webprogramozás
Mai cél
- JavaScript alapok (korábbi ismeretek JS-ben)
- adatábrázolás (sorozatok, rekordok)
- programozási tételek (vezérlési szerkezetek)
- új köntösben is
Adottak a Webprogramozás tárgy eredményei név-jegy párokban. Add meg az 5-öst szerző hallgatók nevét!
Környezet
filter.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Filter</title>
</head>
<body>
✒><script src="data.js"></script>
<script src="filter-01.js"></script>
<script src="filter-02.js"></script><✒
</body>
</html>Adatábrázolás
data.js
const wpResults = [
{ name: "Henry Edwards", grade: 3 },
{ name: "John Young", grade: 2 },
{ name: "Noah Williams", grade: 4 },
{ name: "Julie Moore", grade: 5 },
{ name: "Jeffrey Roberts", grade: 5 },
{ name: "Brandon Turner", grade: 3 },
{ name: "Mia Wright", grade: 5 },
{ name: "Catherine Mitchell", grade: 4 },
{ name: "Kevin Johnson", grade: 4 },
{ name: "Thomas James", grade: 5 },
];Megoldás 1. (régi)
filter-01.js
function filterGrade5(students) {
const result = [];
for (const student of students) {
if (✒>student.grade === 5<✒) {
result.push(✒>student.name<✒);
}
}
return result;
}
console.log( filterGrade5(wpResults) );Megoldás 2. (új, ajánlott)
filter-02.js
const result = wpResults
.filter(student => student.grade === 5)
.map(student => student.name);
console.log(result);Kliensoldali webprogramozás
- Böngésző
- Dokumentum
- JavaScript nyelv
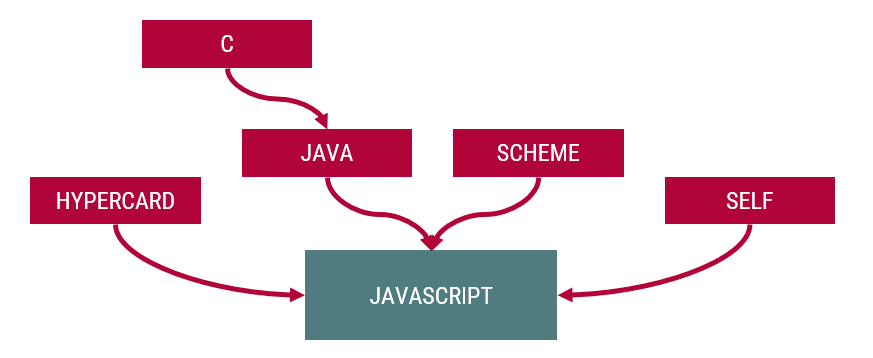
JavaScript története
- 1991: világháló születése
- 1993: első grafikus böngészők
- 1994: Netscape Navigator böngésző
- 1995 áprilisa: Netscape
- Brendan Eich: olyan programozási nyelv, amelyekkel interaktívvá tehetők weboldalak
- 1995 decembere: bejelentik a JavaScriptet

- 1996-1999: I. böngészőháború ⚔️ (Netscape vs IE)
- A kliensoldal megbízhatatlan
- 1999-2004: Sötét középkor
- Szerveroldali technológiák fejlődése
- 2004-2017: II. böngészőháború ⚔️ (IE vs Firefox, Opera, …)
- 2006-: JavaScript újrafelfedezése (AJAX, jQuery)
- 2008: Google Chrome
- III. böngészőháború ⚔️ (JS sebessége)
- 2009-: parancssori JavaScript (Node.js)
- 2017: Google Chrome 👑 (Chromium)
Név és szabvány
- Elnevezések:
- LiveScript: eredeti név
- JavaScript: marketing miatt a Java programozók átcsábítására (web Visual Basic-je)
- Szabvány: ECMAScript
- Európai Informatikai és Kommunikációs Rendszerek Szabványosítási Szövetsége (ECMA)
- Microsoft
- JScript
ECMAScript verziók
- 1997: 1. verzió
- 1999: 3. verzió
- 2009: 5. verzió (ES5)
- hibajavítások, apróbb fejlesztések
- 2015: 6. verzió (ES6, ECMAScript 2015)
- nagyobb fejlesztések, modern nyelvi tulajdonságok
- 2016: 7. verzió (ES7, ECMAScript 2016)
- 2017: 8. verzió (ES8, ECMAScript 2017)
- …
Stages: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 → szabvány
Fejlesztőeszközök
Szerkesztők, böngészők, eszköztárak, dokumentáció
Szerkesztők
- Kódszerkesztők
- Notepad++
- Sublime Text 3
- Atom
- Visual Studio Code
- Integrált fejlesztőkörnyezetek (IDE)
- NetBeans IDE
- Visual Studio
- WebStorm
Tetszőleges modern kódszerkesztő használható
Böngészők
- Google Chrome (Blink)
- Mozilla Firefox (Gecko, Quantum)
- Microsoft Edge (Chromium, Blink)
- Opera (Chromium, Blink)
- Safari (Webkit)
Tetszőleges modern böngésző használható
Megjelenítő motorok kis történelme:
KHTML (Konqueror) → Webkit (Safari) → Blink (Chrome)
Webfejlesztési eszközök
- Webfejlesztő eszköztár (F12)
- Elemek
- JavaScript konzol (
console) - Debugger
- Erőforrások
- Hálózati forgalom
- Teljesítményprofilozás
- Parancssori eszközök
Dokumentáció
- Hivatalos dokumentáció az ECMAScript szabvány
- Mozilla Developer Network: JavaScript
- Főoldal
- JavaScript referencia
- JavaScript guide
- Firefox specifikus dolgok, de a dokumentáció megfelelően jelzi
Futtató környezet
Futási környezet
A JavaScriptnek szüksége van egy futtató környezetre
- Böngésző
- Parancssor (Node.js)
Hova írhatjuk a kódot?
- JavaScript konzolba (böngésző)
- Az adott oldal kontextusában értelmezésre kerül
- Kipróbálásra jó
- HTML kódba (böngésző)
- Inline szkript,
<script>tag, bárhova rakhatjuk - Külső állományba,
<script>tag src attribútumával töltjük be
- Inline szkript,
- Parancssori értelmezőbe (parancssor, Node.js)
JavaScript kód helye
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Webfejlesztés 2.</title>
<script>
//JavaScript code here
</script>
<script src="jscode.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//JavaScript code here
</script>
<p>Hello world!</p>
<script src="jscode2.js"></script>
</body>
</html>JavaScript kód helye
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- ... -->
</head>
<body>
<!-- ... -->
<script src="code.js"></script>
</body>
</html>A JavaScript nyelv
Alapok
Mintaként szolgáló nyelvek
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//declaration
const int n=5;
double x[]={1,3,5,7,9};
double s;
//process
s=0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
s=s+x[i];
}
//write output
cout<<"Sum: "<<s<<endl;
return 0;
}
//declaration
const x=[1,3,5,7,9]
let s
//process
s=0
for(let i=0; i<x.length; i++) {
s=s+x[i]
}
//write output
console.log('Sum: ', s)C++
- Erősen típusos
- Fordított
- Általános célú programozási nyelv
JavaScript
- Dinamikusan típusos
- Interpretált
- Szkriptnyelv
Dinamikusan típusos
- A változók típusa a benne tárolt érték típusától függ
- Vagy másképp: a típusok az értékekhez tartoznak, nem a változókhoz.
- Automatikus típuskonverziók (lehetőleg kerüljük)
a = 'alma';
a = 12;
a == '12'; //trueInterpretált
- A böngészőben futó értelmező értelmezi a JavaScript kódsorokat sorról sorra
- Nincs fordítási fázis, nem a lefordított kód fut
- Minimális előfeldolgozás történik
- A kód a hibáig lefut, ott elakad:
- Az adott
<script>blokk futása megáll - A
<script>blokk után folytatódik az oldal betöltése
- Az adott
További jellemzők
- Kis és nagybetűk különböznek (case sensitive)
- Nincs főprogram (
main) - Nincs input/output (csak API-kon keresztül)
- Nincs fájlkezelés (csak API-kon keresztül)
- Objektumorientált
- Prototípusos
- Automatikus pontosvessző beszúrás ❗
let a = 12 // --> let a = 12;
a = a + 1 // --> a = a + 1;Típusok
Primitív értékek
null |
undefined |
Egyszerű típusok
| Logikai | Boolean |
| Szám | Number |
| Szöveg | String |
Összetett típusok
| Objektum | Object |
| Tömb | Array |
| Függvény | Function |
Literálformák
Adott típus megjelenési formája
// Logikai literál
true
false
// Szám literál
12
12.34// Szöveg literál
'Szöveg'
"Szöveg"
`Szöveg`
`Tetszőleges ${kifejezés}`
'Idézőjelben "így" macsakörmölök'
"Macskakörömben 'így' idézek"
'Idézőjelben \' idézőjel'
"Macskakörömben \" macskaköröm"
'Escape: \t \n \\ 'Változók
varlet,constkulcsszóval deklarálunk új változót- ezek elhagyásával → globális változó – KERÜLENDŐ!!!
- Ha nincs kezdőérték → undefined
let nev = 'Győző'; // 'Győző'
let masik; //undefinedOperátorok
- Aritmetikai operátorok
+,-,*,/,%,++,--, unáris-, unáris+
- Értékadás operátorai
=,*=,/=,%=,+=,-=, stb.
- Összehasonlító operátor
===,!==,==,!=,>,>=,<,<====és!==típus és érték szerint==és!=érték szerint (automatikus konverziók)
12 == '12' // true
12 === '12' // falseOperátorok
- Logikai operátorok
&&,||,!
- Szövegösszefűzés operátorai
+,+=
- Bitenkénti operátorok
&,|,^,~,<<,>>,>>>
- Speciális operátorok
? :feltételes operátor,több kifejezés végrehajtása egy utasításban, visszatérési értéke az utolsó kifejezés
Vezérlési szerkezetek
// Elágazás
if (felt) {
utasítások
}
if (felt) {
utasítások
} else {
utasítások
}// Többirányú elágazás
switch(kifejezés) {
case érték1:
utasítások
break;
case érték2:
utasítások
break;
default:
utasítások
}// Ciklusok
while (felt) {
utasítások
}
do {
utasítások
} while (felt);
for (let i=1; i<=n; i++) {
utasítások
}A JavaScript nyelv
Függvények
int factorial(int n) {
int f = 1;
for (int i=2; i<=n; i++) {
f *= i;
}
return f;
}function factorial(n) {
let f = 1;
for (let i=2; i<=n; i++) {
f *= i;
}
return f;
}Alapértelmezett értékek
// function declaration
function add(a, b = 3) {
return a + b;
}
// function call
add(40, 2) // 42
add(10) // 13
add(50, 20, 10) // 70
add() // NaNLétrehozási formák
// function declaration
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
// function expression
const add = function (a, b) {
return a + b;
}
// fat arrow
const add = (a, b) => {
return a + b;
}
const add = (a, b) => a + b;Literálforma
Ahogy egy kifejezésben megjelenhet
function (a, b) {
return a + b;
}
// or
(a, b) => a + b
// for example
const add = (a, b) => a + bFüggvény mint paraméter
function countA(str) {
let count = 0;
for (const c of str) {
if (c === 'a') {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
console.log( countA("apple") ) // 1Függvény mint paraméter
function count(str, fn) {
let db = 0;
for (const c of str) {
if (fn(c)) {
db++;
}
}
return db;
}
console.log(
count("apple", c => c === 'a')
)A JavaScript nyelv
Tömb
Létrehozás, olvasás
Literálforma: []
// creation
const uresTomb = [];
const tomb = [12, 'alma', true];
// referencing an element
tomb[0]; // => 12;
tomb[1]; // => 'alma';
tomb[2]; // => true;
// length
tomb.length; // => 3Módosítás
const tomb = [12, 'alma', true];
// modification
tomb[0] = 13;
// new element at the end
tomb.push("new");
// new element somewhere (not recommended)
tomb[100] = 'far away';
tomb.length; // => 101
tomb[99]; // => undefined
// deleting (size remains the same)
delete tomb[1];
tomb[1]; // => undefined
tomb.length; // => 101Mátrix
Tömbök tömbje
const m = [
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
];
m[1][2]; // => 6Iteratív feldolgozás
const gyumolcsok = [
'alma',
'korte',
'szilva'
];
//A gyümölcsök kiírása a konzolra
for (let i = 0; i < gyumolcsok.length; i++) {
console.log(gyumolcsok[i]);
}
// for..of ciklus (ES6)
for (const gyumolcs of gyumolcsok) {
console.log(gyumolcs);
}Tömb műveletek
pop(),push(e),shift(),unshift(e)- végéről, végére, elejéről, elejére
reverse()- megfordít
splice(honnan, mennyit)- kivág
join(szeparátor)- szöveggé fűz
indexOf(elem)- keresés
includes(elem)- eldöntés
const t = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
t.push(6); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
t.pop(); // --> 6, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
t.unshift(0); // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
t.shift(); // --> 0, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
t.reverse(); // [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
t.splice(2, 1); // [5, 4, 2, 1]
t.join('###'); // "5###4###2###1"Tömbfüggvények
Programozási tételek megvalósítása
forEach: általános ciklussome: eldöntésevery: optimista eldöntésmap: másolásfilter: kiválogatásreduce: összegzés (sorozatszámítás)find: keresés (elem)findIndex: keresés (index)
Példa – kiválogatás
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
function filter(x, fn) {
const out = [];
for (const e of x) {
if (fn(e)) {
out.push(e);
}
}
return out;
}
const evens = filter(numbers, e =>e % 2 === 0);
// instead
const evens = numbers.filter(e =>e % 2 === 0);Példa – összegzés
function sum(x) {
let s = 0;
for (const e of x) {
s = s + e;
}
return s;
}
// instead
x.reduce((s, e) => s + e, 0);Referenciatípus
// const reference, content dynamic
const x = []
x.push(10)
// copy reference
const x1 = [1, 2, 3]
const x2 = x1
x2[1] = 20
console.log(x1) // --> [1, 20, 3]
// shallow copy
const x3 = [1, 2, 3]
const x4 = x3.slice()
// const x4 = x3.concat()
x4[1] = 20
console.log(x3) // --> [1, 2, 3]
const m1 = [
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
]
const m2 = m1.concat()
m2[0][1] = 20
console.log(m1[0]) // --> [1, 20, 3]
// deep copy
const m3 = [
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
]
const m4 = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(m3))
m4[0][1] = 20
console.log(m3[0]) // --> [1, 2, 3]Destructuring and spread
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const a = numbers[0];
const b = numbers[1];
// instead
const [a, b] = numbers;
// default values
const [a = 10, b = 20] = [100] // a:100, b:20
// rest
const [a, b, ...rest] = numbers; // --> rest:[3, 4, 5]
// swapping variables
[a, b] = [b, a]
// ignoring
const [a,,b] = numbers; // a:1, b:3
// spread
const a = [1, 2, 3];
const b = [9, ...a, 10]; // b:[9, 1, 2, 3, 10]A JavaScript nyelv
Objektum
Objektum
- Kulcs-érték párok gyűjteménye
- Asszociatív tömbhöz hasonlít (hash)
- Rekord, osztálypéldány szimulálható
- JavaScriptben nagyon fontos szerepük van
- Majdnem minden objektum
- Ha az érték függvény → metódus
Létrehozás, olvasás
Literálforma: { }
// creation
const uresObj = {};
const obj = {
mezo1: 12,
'mezo2': 'alma',
};
// referencing
obj.mezo1; // => 12
obj['mezo1']; // => 12Módosítás
const obj = {
mezo1: 12,
'mezo2': 'alma',
};
// modification
obj.mezo2 = 'korte';
// extending
obj.mezo3 = true;
// deletion
delete obj.mezo1;
obj.mezo1; // => undefinedMetódus (függvény mint adattag)
const obj = {
data: 42,
metodus: function () {
console.log('Foo: ', this.data);
},
metodus2() {
console.log('Foo: ', this.data);
}
};
obj.metodus();
obj.metodus2();Getter és setter
const obj = {
_data: 42,
get data() {
return _data;
},
set data(value) {
_data = value;
}
};
obj.data = 52;
obj.data; // 52Dinamikus mezőnév
// Computed property names
const prop = 'foo';
const o = {
[prop]: 'something',
['b' + 'ar']: 'new'
};
o.foo; // 'something'
o.bar; // 'new'Példák
//Tömb az objektumban
const zsofi = {
kor: 7,
kedvencEtelek: [
'krumplipüré',
'rántott hús',
'tejberizs'
]
};
//Elem elérése
zsofi.kedvencEtelek[1];
// => 'rántott hús'//Objektum az objektumban
const david = {
kor: 4,
cim: {
iranyitoszam: '1241',
varos: 'Budapest',
utca: 'Egyszervolt utca',
hazszam: 63
}
};
//Elem elérése
david.cim.utca;
// => 'Egyszervolt utca'Feldolgozás
const matyi = {
kor: 1.5,
fiu: true,
cuki: true
}
// Feldolgozás a for..in ciklussal
for (const i in matyi) {
console.log(i, matyi[i]);
}
// Eredmény
// => kor 1.5
// => fiu true
// => cuki trueAdatszerkezetek modellezése
//C++ vector --> JS tömb
const kutyuk = [
'telefon',
'fülhallgató',
'pendrive',
'e-könyv olvasó'
];//C++ struct --> JS objektum
const hallgato = {
nev: 'Mosolygó Napsugár',
neptun: 'kod123',
szak: 'Informatika BSc'
};//Rekordok tömbje
const hallgatok = [
{
nev: 'Mosolygó Napsugár',
neptun: 'kod123',
szak: 'Informatika BSc'
},
{
nev: 'Kék Ibolya',
neptun: 'kod456',
szak: 'Informatika BSc'
}
];Adatszerkezetek modellezése
//Tömböt tartalmazó rekordok tömbje
const hallgatok = [
{
nev: 'Mosolygó Napsugár',
neptun: 'kod123',
szak: 'Informatika BSc',
targyak: [
'Programozás',
'Webfejlesztés 2.',
'Számítógépes alapismeretek'
]
},
{
nev: 'Kék Ibolya',
neptun: 'kod456',
szak: 'Informatika BSc',
targyak: [
'Programozás',
'Webfejlesztés 2.',
'Diszkrét matematika',
'Testnevelés'
]
}
];Referenciatípus
// const reference, content dynamic
const o = {}
o.field1 = 12
// copy reference
const o1 = { field1: 2 }
const o2 = o1
o2.field1 = 20
console.log(o1) // --> { field1: 20 }
// shallow copy
const o3 = { field1: 2 }
const o4 = {}
for (let key in o3) {
o4[key] = o3[key]
}
// Object.assign(o4, o3)
o4.field1 = 20
console.log(o3) // --> { field1: 2 }
const n1 = {
field1: { subfield1_1: 1 },
field2: { subfield2_1: 2 },
}
const n2 = Object.assign({}, n1)
n2.field2.subfield2_1 = 20
console.log(n1.field2) // --> { subfield2_1: 20 }
// deep copy
const n3 = {
field1: { subfield1_1: 1 },
field2: { subfield2_1: 2 },
}
const n4 = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(n3))
n4.field2.subfield2_1 = 20
console.log(n3.field2) // --> { subfield2_1: 2 }Destructuring and spread
const o = {
a: 42,
b: 28,
}
const a = o.a
const b = o.b
// instead
const {a, b} = o;
// renaming
const {a: c, b: d} = o;
// default values
const {a = 10, b = 20} = {a: 42};
const {a: c = 10, b: d = 20} = {a: 42};
// rest
const o = {
a: 42,
b: 28,
c: 12
};
const {a, ...rest} = o; // rest={b:28, c:12}Destructuring and spread
// nested objects
const david = {
kor: 4,
cim: {
iranyitoszam: '1241',
varos: 'Budapest',
utca: 'Egyszervolt utca',
hazszam: 63
}
};
const { cim: { utca }} = davidclass (ES6)
class Rectangle {
constructor(height, width) {
this.height = height;
this.width = width;
}
// Getter
get area() {
return this.calcArea();
}
// Method
calcArea() {
return this.height * this.width;
}
}
const square = new Rectangle(10, 10);
console.log(square.area); // 100class – publikus mezők
class Product {
name;
tax = 0.2;
basePrice = 0;
price;
constructor(name, basePrice) {
this.name = name;
this.basePrice = basePrice;
this.price = (basePrice * (1 + this.tax)).toFixed(2);
}
}Tesztelés
Példa
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}Tesztelés a konzolon
Tesztelés a kódban
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
// console.assert
console.assert(add(3, 2) === 5, '3 + 2 should be equal 5');
console.assert(add(10, 0) === 10, '10 + 0 should be equal 10');Összefoglalás
- C++ → JavaScript
- Adatszerkezetek
- egyszerű: logikai, szám, szöveg
- összetett: tömb, objektum, függvény
- Programozási tételek tömbfüggvényekként
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (i % 2 === 0) {
console.log(i);
}
}const numbers = [3, 1, -1, 4, 6, -3]
console.log( numbers.filter(e => e < 0) ) // [-1, -3]const king = {
name: 'Mathias Rex',
from: 1458,
to: 1490,
}